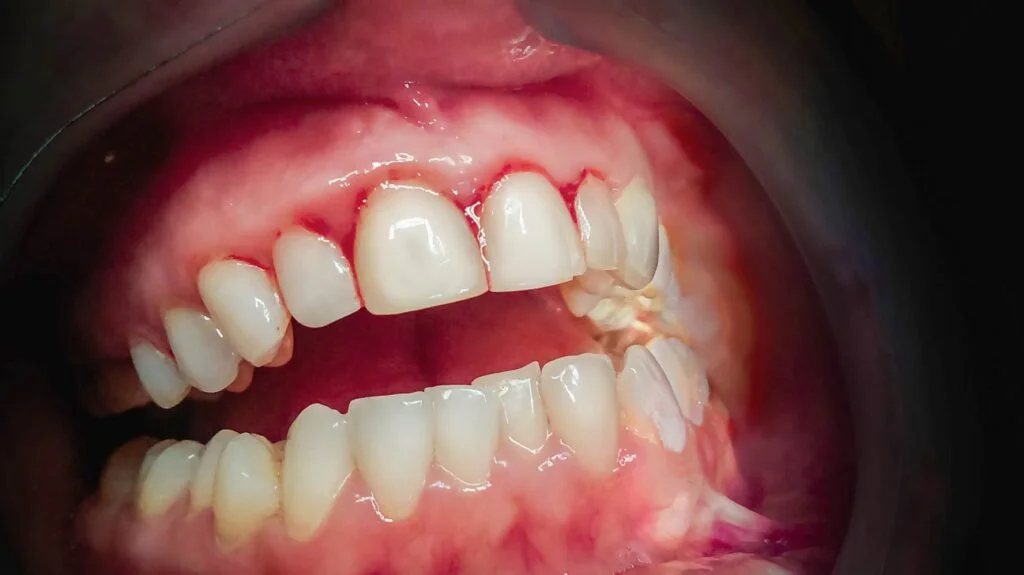
Gingivitis, a common oral health issue affecting adults, is increasingly becoming a concern in pediatric dentistry as well. Gingivitis in children, often referred to as pediatric gingivitis, can have several causes, ranging from poor oral hygiene to underlying health conditions.
Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the appropriate treatments are essential for parents and caregivers in managing and preventing pediatric gingivitis.
Causes of Pediatric Gingivitis:
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the accumulation of plaque and bacteria along the gumline, causing inflammation and gingivitis.
Plaque Buildup: Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, can accumulate on teeth and gums, leading to irritation and inflammation of the gingival tissue.
Dietary Habits: High sugar consumption, especially from sugary snacks and beverages, can contribute to plaque formation and increase the risk of gingivitis.
Genetic Factors: Some children may be predisposed to gum disease due to genetic factors, making them more susceptible to developing gingivitis.
Systemic Conditions: Certain systemic conditions such as diabetes or immune disorders can increase the risk of gingivitis in children by affecting their immune response and oral health.
Symptoms of Pediatric Gingivitis:
Swollen Gums: Inflamed gums that appear red, swollen, or puffy may indicate gingivitis in children.
Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing can be a sign of gingivitis.
Bad Breath: Persstent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be a symptom of gingivitis caused by bacteria in the mouth.
Receding Gums: Gingivitis can cause the gums to recede or pull away from the teeth, exposing the tooth roots.
Tender Gums: Children with gingivitis may experience tenderness or discomfort in the gums, especially when chewing or brushing.
Treatments for Pediatric Gingivitis:
Improved Oral Hygiene: Encouraging proper brushing and flossing techniques is crucial in managing pediatric gingivitis. Children should brush their teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent gum inflammation.
Regular Dental Checkups: Routine dental visits allow dentists to monitor oral health, identify early signs of gingivitis, and provide professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
Dietary Modifications: Limiting sugary snacks and beverages can help reduce plaque formation and lower the risk of gingivitis in children. Encouraging a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and calcium can also support overall oral health.
Professional Cleanings: In cases of more advanced gingivitis, a dentist may perform a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooth the tooth roots to prevent bacteria buildup. Make sure to visit one of the best Winermere dental clinics for this purpose.
Antibacterial Mouthwash: Dentists may recommend antimicrobial mouth rinses to help reduce bacteria in the mouth and alleviate gum inflammation in children with gingivitis.
Orthodontic Evaluation: Misaligned teeth or bite issues can make it difficult to maintain proper oral hygiene, increasing the risk of gingivitis. An orthodontic evaluation may be necessary to address any alignment issues and improve oral hygiene practices.
Preventing Pediatric Gingivitis:
Prevention is key in managing pediatric gingivitis and maintaining optimal oral health in children. Parents and caregivers can take the following steps to prevent gingivitis:
- Promote Good Oral Hygiene Habits: Teach children proper brushing and flossing techniques from an early age and supervise their oral care routines.
- Encourage a Healthy Diet: Limit sugary snacks and beverages and encourage a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals essential for oral health.
- Schedule Regular Dental Checkups: Routine dental visits allow dentists to detect and address oral health issues early, preventing the progression of gingivitis.
- Lead by Example: Set a positive example by prioritizing your own oral health and demonstrating good oral hygiene habits to your children.
In conclusion, pediatric gingivitis is a common but preventable condition that requires attention and proactive management. By promoting good oral hygiene practices, maintaining a healthy diet, and seeking regular dental care, parents and caregivers can help prevent gingivitis and ensure the long-term oral health of their children.
Early detection and treatment of gingivitis are essential in preventing more serious oral health problems in the future.