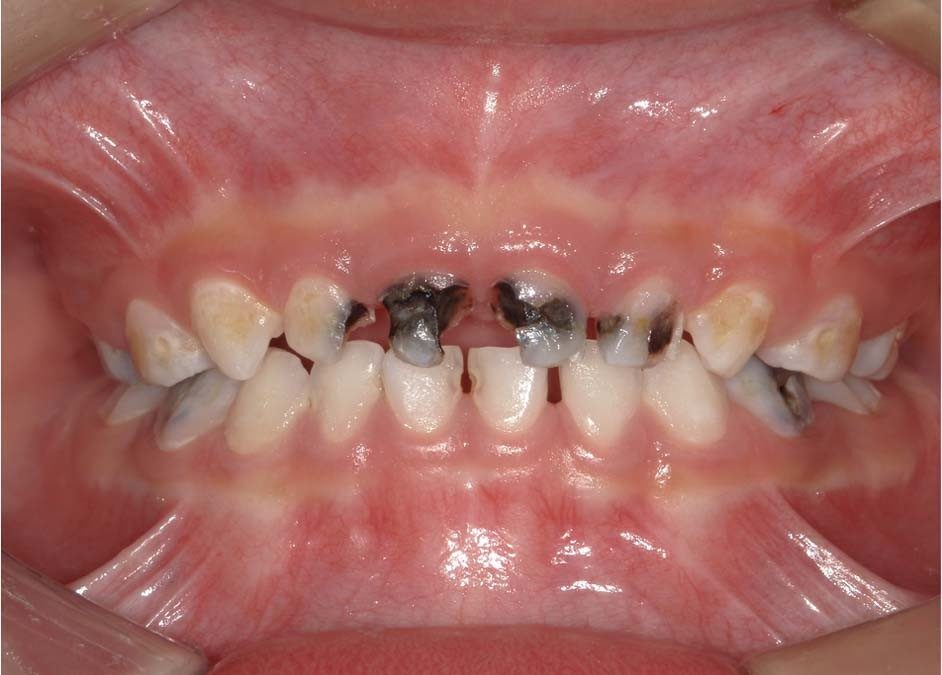
Cavities in early childhood can be a significant concern, not only for the child’s dental health but also for their overall well-being. Early childhood cavities, also known as baby bottle tooth decay or early childhood caries, can lead to pain, infection, difficulty eating, and even developmental issues if left untreated.
Fortunately, many strategies can help prevent early childhood cavities and promote good oral health from the start. However, the best solution is to schedule a consultation session with one of the best
at the earliest.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore various preventive measures parents and caregivers can take to safeguard their child’s dental health.
Start Early:
Dental care should begin even before your child’s first tooth emerges. Use a clean, damp cloth to gently wipe your baby’s gums after feedings to remove bacteria. Once teeth start appearing, switch to a soft-bristled infant toothbrush and gently brush their teeth twice a day.
Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks:
Sugary foods and drinks are the main culprits behind tooth decay. Avoid giving your child sugary snacks and drinks, especially between meals. If you do offer sweets, opt for healthier alternatives like fruits. Additionally, never let your child fall asleep with a bottle containing anything other than water, as this can lead to prolonged exposure to sugars and increase the risk of cavities.
Practice Good Oral Hygiene:
Teach your child the importance of proper oral hygiene from a young age. Encourage them to brush their teeth using fluoride toothpaste twice a day, making sure to reach all surfaces of the teeth.
Supervise brushing until they are old enough to do it effectively on their own, usually around age 6 or 7. Flossing should also become a regular part of their oral hygiene routine once their teeth start touching.
Schedule Regular Dental Check-ups:
Regular dental check-ups are crucial for detecting and addressing any dental issues early on. Schedule your child’s first dental visit by their first birthday or within six months of their first tooth erupting, whichever comes first.
Routine visits every six months allow the dentist to monitor your child’s oral health and provide preventive treatments such as fluoride varnish application or dental sealants if necessary.
Ensure Sufficient Fluoride Intake:
Fluoride is a mineral that strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent cavities. Ensure your child receives an adequate amount of fluoride through fluoridated drinking water, fluoride toothpaste, and professional fluoride treatments at the dentist’s office if recommended.
However, be cautious not to exceed the recommended fluoride intake, as excessive fluoride can lead to dental fluorosis, a condition that causes white spots to develop on the teeth.
Lead by Example:
Children often learn by observing their parents’ behaviors. Set a positive example by prioritizing your own oral health and demonstrating good oral hygiene habits. Brush and floss your teeth together as a family, making it a fun and interactive activity rather than a chore.
Be Mindful of Medications:
Some medications, such as certain antibiotics and antihistamines, can increase the risk of cavities by reducing saliva production or altering its composition. If your child is taking medication, consult with their healthcare provider or dentist about any potential oral health implications and strategies to mitigate them.
Address Dental Habits:
Thumb sucking, pacifier use, and prolonged bottle-feeding can contribute to dental problems if they persist beyond infancy. Encourage your child to break these habits as they get older to prevent misalignment of teeth and other dental issues.
Monitor Diet and Nutrition:
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in oral health. Provide your child with nutritious meals and snacks rich in vitamins and minerals essential for healthy teeth and gums. Limit starchy and sticky foods that can cling to the teeth and promote bacterial growth.
Stay Informed:
Stay informed about the latest recommendations and guidelines for pediatric dental care. Keep up with advancements in oral health research and consult with your child’s dentist or pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about their dental health.
By following these preventive measures and incorporating good oral hygiene habits into your child’s daily routine, you can significantly reduce their risk of developing early childhood cavities and set them on the path to a lifetime of healthy smiles. Remember, early intervention and consistent dental care are key to ensuring optimal oral health for your child.